Computer Science and Digital Information Technology
Computing and Digital Information Technology
Introduction to the Team:
Mr. A. Hussain – Subject Leader
Mr. D. Ahmed – Teacher of Computing
Subject Aims/Intent:
Computing
Famous Quote
“Computers themselves, and software yet to be developed, will revolutionise the way we learn” Steve Jobs
Computing at Ormiston Sandwell Community Academy aims to enable students to develop skills and knowledge in Computer Science and Digital Technologies to prepare them for a future in a world where the use of this technology is fully embodied. We wish to enthuse students to have an understanding far deeper than the interface that they currently operate. We aim to enable students to develop a love of learning for the subject and an understanding that there are no limits to their own development in programming and IT. Students will develop transferable IT skills that can be used across different curriculums to support their academic skills and build their resilience, independence, and cultural capital.
Our students at OSCA have grown up in a digital world. Technology and the digital aspects of our lives are forever expanding.
It is vital our students have an understanding of how digital information and technology will impact their lives, and play a part in their future.
In Digital Information Technology we ensure that all students have the opportunity to explore a large range of topics.
Overall Purpose of the Subject:
- Computing and Digital IT provide an invaluable understanding and practical knowledge of Computer Systems in a fast changing modern environment.
- In a competitive market, sound Computing and ICT skills are much sought after and provide candidates with a skill set that will enable them to work in a vast number of areas.
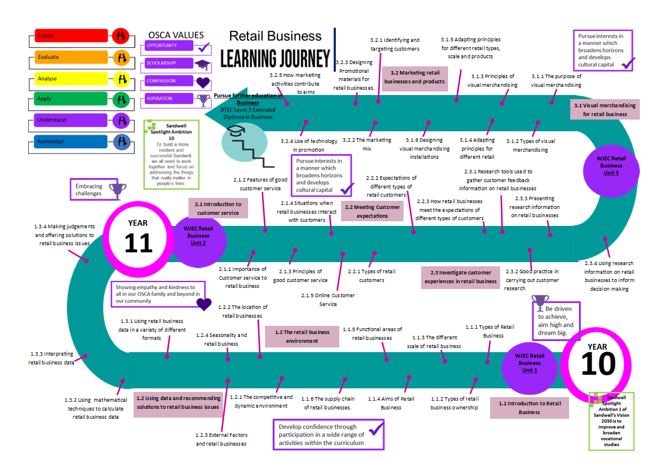
Retail Business
To deliver an engaging and inspiring 2-year course which will embed students with key skills and knowledge making them ready for the world of work or to continue with their Retail or Business pathway at KS5 studying A-level Business, A level Economics or BTEC Business. The WJEC in Retail Business will prepare our students for a future in one of the most important employment sector in the UK. We aim to provide them with opportunity to investigate a range of retailers from large chains to and department stores through to independent and virtual stores.
The Retail Business curriculum prepares students to become independent and critical thinking. A range of topics allow students to develop an understanding and appreciation of how the retail industry works. These themes are explored through different styles. Furthermore, the subject in our department embraces our OSCA core values by promoting a sense of self-worth, encouraging confidence and resilience, and developing relationships. I believe the study of Retail Business promotes an overall appreciation of how the industry works in various formats both inside and outside of the classroom developing discipline, control and focus to grow into well rounded adults. Retail Business offers a range of trips which include a visit to Bullring shopping centre and different retail businesses. I am proud to offer coursework catch up club for the students. These activities help students to understand the value of the course as its equipping young people with the knowledge and skills with which to forge careers in this lucrative and diverse sector is enormous.
Subject Implementation:
Computing
Key Stage 3
Year 7
Autumn Term
Using Computers Safely Effectively and Responsibly – Students will enter the world of computer safety. They will discover how to stay safe when in the IT rooms and also when using a range of devices at home. They will discover how they can remain safe when using the internet and social media.
Spring Term
Understanding Computers – Students will then move onto finding out how computing devices work. They will delve into how computers process data using binary and learn how to convert binary themselves. They will consider how we can keep our data safe using a range of back up methods. Finally, they will dive into the world of emerging technologies and consider where the technological world will lead us to next.
Summer Term
First Steps in Small Basic – Students will embark on their first written programming unit where they will learn the concepts of computer programming. They will consider using the correct syntax and how to ensure their programs are maintainable through indentation and comments. They will be able to use both text and graphics windows when using small basic and explain the programming constructs.
Year 8
Autumn Term
Computer Crime and Cyber Security – Students will learn how they can keep themselves safe from online threats such as phishing, Trojan horse scams and malware. They will consider how to keep their accounts and personal data safe using methods such as strong passwords and understanding the Data Protection Act. They will explore the dangers of hacking and the law that it breaks, The Computer Misuse Act. They will also research a well-designed workstation and how to protect themselves from RSI, eye strain and back problems from using computers. Finally, they will discover what an employer must do to protect their employees.
Spring Term
Python Programming – Students will recap and build upon skills learnt in year 7 during the Small Basic unit. They will look at the structure of programs including, sequence, selection and iteration, use of arrays, functions and procedures. Students will develop their knowledge of variables and use variables effectively within programs. Students will be able to explain how their programs work by including comments.
Summer Term
Spreadsheet Modelling – Students will learn about computer models and how they can be used to make predictions using data. They will analyse data using a range of methods including ‘What if’ scenarios, conditional formatting, validation, macros and charts.
Year 9
Autumn Term
Logic and Languages – Students will recap and develop the knowledge learnt during the understanding computers unit in year 7. They will learn about computational thinking (abstraction, decomposition, pattern recognition and algorithmic thinking). They will develop their knowledge of Boolean operators and apply this to logic diagrams. They will learn about sorting and searching algorithms and how to perform these. Students will understand how images and sound a represented in binary within a computer.
Spring Term
Business and Digital Literacy – Students will be introduced to Business while developing their digital literacy skills. They will learn about different types of business, how businesses are run and the different ways in which businesses can be advertised. They will also develop their research skills, project planning skills, evaluation and testing of products.
Summer Term
Graphics – Students will learn about different types of graphics (vector and bitmap). They will learn a range of skills in a graphic design program in order to create their own vector graphics. They will be given a scenario and will need to plan, create an evaluate a vector graphic to meet the requirements of the scenario.
Key Stage 4
Throughout Key Stage 4 we offer the BTEC Tech Award in Digital Information Technology, GCSE Computer Science (OCR)and the WJEC in Retail Business. The BTEC course will continue to develop the skills and knowledge learnt during IT topics in KS3. The Computer Science GCSE will continue to develop the skills and knowledge learnt during the Computer Science topics at KS3. The Retail Business qualification introduces them to the word of Retail.
BTEC in Digital Information Technology
Component 1
Students will be introduced to the course and the knowledge and skills that they will learn throughout the 3 years. They will then begin the 1st component of 3 ‘User Interface Design’. Here they will use research skills to analyse a range of existing user interfaces such as menu based interfaces, graphical user interfaces, text based interfaces and speech interfaces on a range of devices such as desktop computers, hand held devices, entertainment systems and domestic appliances.
Students will then develop their project planning techniques to enable them to plan a project to design and create a user interface based on a provided scenario. They will need to show understanding of the different techniques that will ensure a project runs smoothly.
Finally, students will learn the skills needed to create the interface that they have designed. They will use the plans that they have created to ensure that they have a consistent interface that follows the design principles that have been learnt.
Component 2
Students will investigate the role and impact of using data on individuals and organisations. They will consider the characteristics of data and information, learn how to represent information. They will ensure data is suitable for processing. They will learn a range of data collection methods and sampling. They will analyse the quality of information and its impact on decision making. Finally, they will look at the sectors that use data modelling and the threats to individuals when it comes to data collection.
In the second part of this component students will create a dashboard using data manipulation tools. They will also learn about the different data manipulation methods. They will show data summaries from the data set and consider appropriate presentation methods and features.
In the final part of this component students will draw conclusions and review data presentation methods. They will consider trends, patterns, anomalies and possible errors. They will then use this to make recommendations based on the data analysed. They will also consider how presentation affects someone’s understanding of the data.
Component 3 (Exam Component)
During the exam component students will learn about effective digital working practices. They will discuss modern technologies such as communication and cloud technologies. They will then consider the impact of these technologies on modern teams, stakeholders, organisations and individuals. Following this they will investigate the threats to data and how to prevent and manage those threats, the policies that are in place to define responsibilities and outline disaster recovery.
They will analyse the legal and ethical issues surrounding the use of computing devices such as acceptable use, data protection, computer misuse and intellectual property/copyright. Finally, they will evaluate forms of notation for example data flow diagrams, information flow diagrams and flowcharts.
GCSE Computer Science (OCR)
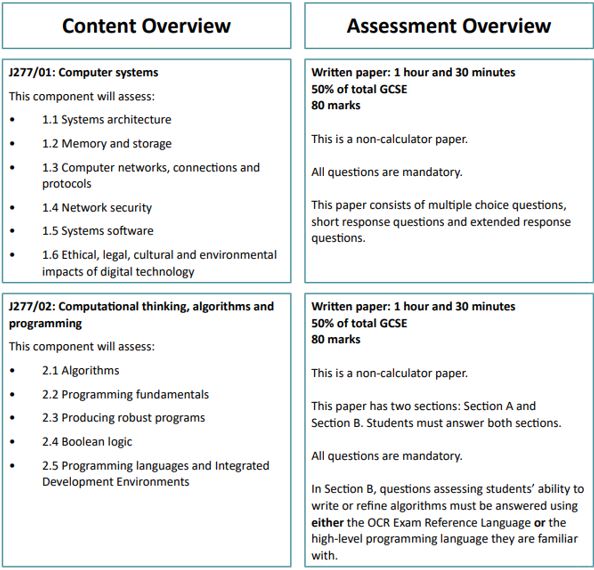
Retail Business
| What do students cover in Key Stage 4? When do they study it? | |
| Year 10 Unit 1: The business of retail Unit 2: Customer service for retail business Mock exam | Year 11 Unit 3: Merchandising and marketing retail products (New Specification) 2023 onwards Unit 1: The business of retail revision and exam practice. Unit 1: Customer Experience (Old Specification 2022-2023) Mock exam Past papers Revision |
Why do they study it in that order?
Natural progression – students need to cover unit 1. This unit introduces students to the competitive and dynamic nature of the retail industry. Students will gain knowledge and understanding of the different types of retail organisations that compete for customers and how these businesses are managed to achieve their aims and provide a continuous supply of products. This will help the students gain basic understanding of customer service for unit 2 and focus on the importance of customer service to retail organisations. Students will study
the importance of visual merchandising and marketing to retail organisations as the final unit in the course. They will be able to link the knowledge and theory from both units to this.
Year 11 consolidate knowledge, exam technique and revision as well as completing unit 3 controlled assessment. Decision has been made in conjunction with the exam board.
How do you ensure students embed knowledge? What do you revisit? When do you revisit it?
Each lesson we regularly revisit prior learning. This is demonstrated in the ‘Do it now / Starter’ tasks. The nature of the course and topics covered require us to go back to previous topics to help consolidate and embed previous knowledge. We incorporate the bigger picture and make links between different topics and skills. This is further embedded into SOW and Power-points e.g., recall and assessment activities. The controlled assessments are a key tool in achieving this, especially for our practical learners. Key Retail Business websites are used such as BBC Business further embed knowledge. Students are given key words which we regularly revisit. They are encouraged to show off their knowledge using Retail Business terminology in exam-based questions. We revisit retail business in Year 11 as part of revision.
Planning:
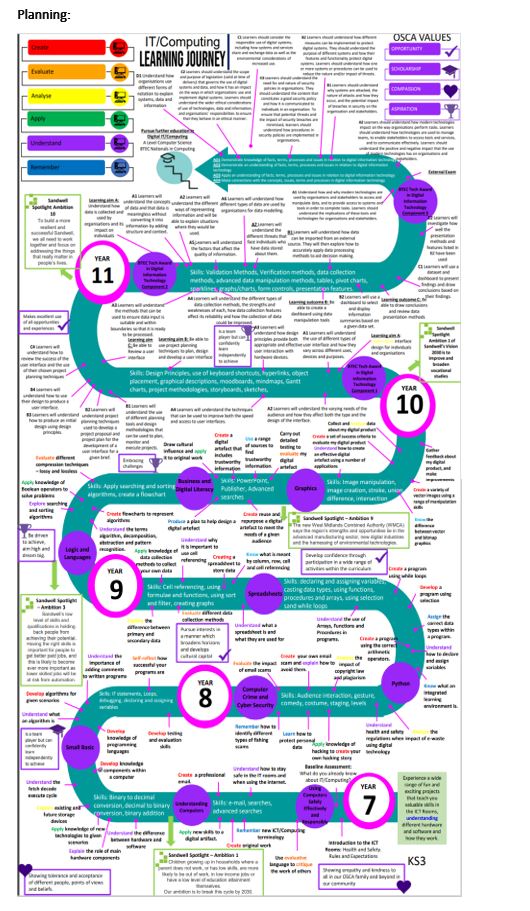
Computer Science KS4 Learning Journey
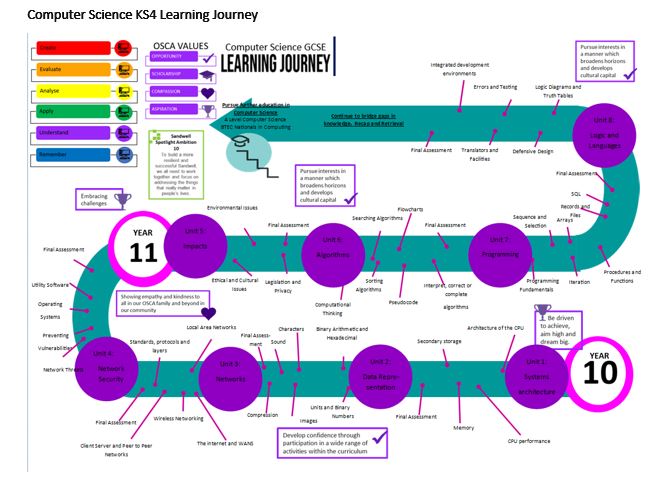
Computer Science KS4 Learning Journey
Assessment:
Computing
Key Stage 3
When students first join us in Year 7 they complete a baseline assessment so that we can see what they already know in computing.
Throughout key stage 3 students complete summative assessments mid-way through each topic (term) and at the end of each topic (term).
As well as this students’ complete quizzes, self-assessment, peer- assessment regularly throughout each term.
Key Stage 4
Students complete the BTEC Tech Award in Digital Information Technology.
Component 1 – Students complete a practice scenario which is assessed regularly to provide feedback for improvement. They will then complete their final assessment for the component which is assessed when completed ready for a grade to be submitted to the exam board.
Component 2 – Students complete a practice scenario which is assessed regularly to provide feedback for improvement. They will then complete their final assessment for the component which is assessed when completed ready for a grade to be submitted to the exam board.
Component 3 – Students will complete practice exam questions throughout the component which will be marked and improved. Students will also completed mock exams to provide an overview of how students are progressing.
Computer Science KS4
Students will complete an end of unit assessment at the end of each of the 8 units. Along side this they will also complete programming challenges and mock exams for both papers.
Retail Business
Key Stage 4
Students complete WJEC Retail Business level1/2.
Unit 1 – Students will complete practice exam questions throughout the unit which will be marked. Students will complete mock exams which will provide an overview of how students are progressing and then sit an external exam.
Unit 2 – Students will complete a practice controlled assessment which is assessed end of each criteria and feedback is given which will help with the real controlled assessment. This is assessed when completed and ready for a grade to be submitted to the exam board.
Unit 3 – Students will complete a practice controlled assessment which is assessed end of each criteria and feedback is given which will help with the real controlled assessment. This is assessed when completed and ready for a grade to be submitted to the exam board.
Homework:
Computing
KS3 – Students are provided with a Homework sheet at the beginning of each half term. From this teachers will provide students with a task from the homework sheet to complete every 2 weeks.
KS4 – Students will be provided with a homework sheet once per week which will recap and build upon what they have learnt during the week in lessons.
Retail Business
KS4_ Students will be provided with a homework sheet/booklet each week. The homework will be a recap and build upon new knowledge that they have learnt or will be learning in the lessons.
Extra- Curricular, Curriculum experiences:
Clubs – We currently offer a coding club at KS3 and revision clubs at KS4.
Useful Websites:
Computing
National Curriculum for computing
https://www.knowitallninja.com/
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/subjects/zqmtsbk (ICT)
Gantt Charts— https://www.wrike.com/blog/project-management-basics-beginners-guide-to-gantt-charts/
Critical Path— https://www.workamajig.com/blog/critical-path-method
Project Methodologies— https://www.guru99.com/waterfall-vs-agile.html
Retail Business
Business news – Business – BBC News
Retail News – Retail Week | News, insight, video and data (retail-week.com)
Drapers Record Fashion retail industry news, trends and analysis | Drapers (drapersonline.com)
Other useful resources:
Computing
Pearson BTEC Tech Award in Digital Information Technology DIT Level 1/2 Component Unit 3 External Assessment Examination IT Learning Aims A to D … Digital Information Technology: Component 3)
BTEC Tech Award Digital Information Technology: Student Book (BTEC Tech Award IT)
BTEC Tech Award Digital Information Technology Component 3: Illustrated Revision and Practice (ClearRevise BTEC Digital Information Technology Level 1/2 Component 3)
Revise BTEC Tech Award Digital Information Technology Revision Guide Kindle (Revise BTEC Tech Award in Digital Information Technology)
CIAG:
Computing
Some examples of careers computing can lead to:
Software Developer
Applications Programmer
Systems Programmer
Multimedia Programmer
Systems Analyst
Computer Sales Support
Database Administrator
IT Technical Support Officer
Computer Security Consultant
Games Developer
IT Consultant
Web Designer
Retail Business
Some examples of careers Retail Business can lead to:
Content writer
Customer service representative
E-commerce web developer
Logistics
Marketing assistant
Marketing management
Retail buyer
Retail management
Sales associate
Social media
Team leader
Visual merchandiser